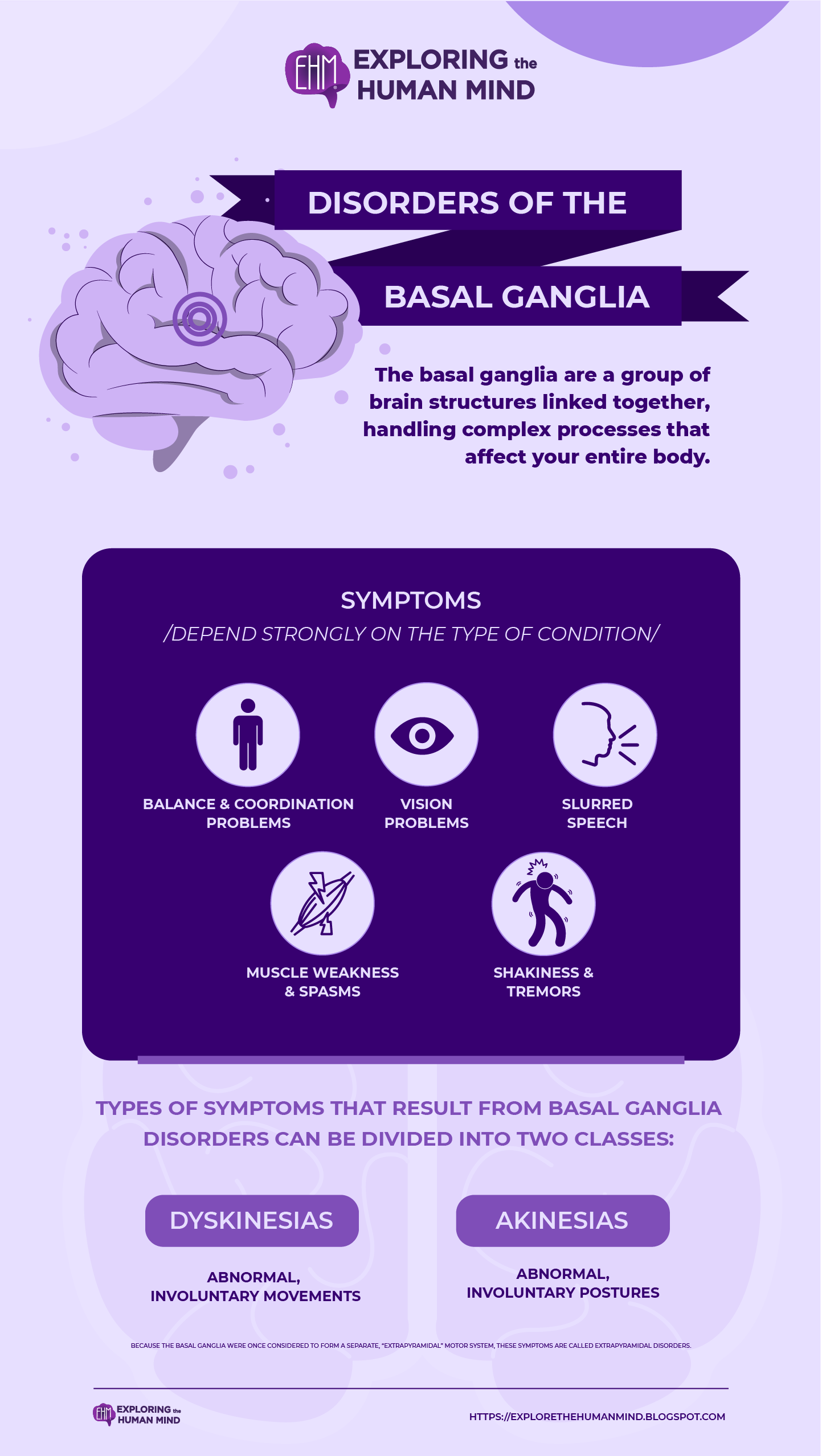
Disorders of the Basal Ganglia
The largest structure in the basal ganglia, the striatum receives signals from parts of the brain using dopamine.
The basal ganglia have historically been considered part of the motor system because of the variety of motor deficits that occur when they are damaged. The types of symptoms that result from basal ganglia disorders can be divided into two classes: dyskinesias, which are abnormal, involuntary movements, and akinesias, which are abnormal, involuntary postures. Because the basal ganglia were once considered to form a separate, “extrapyramidal” motor system, these symptoms are called extrapyramidal disorders.
vectors by Freepick; graphic design by Vadot
Symptoms
The basal ganglia are implicated in many neurological diseases and disorders, from Parkinson’s disease to insomnia to anxiety & depression. The symptoms that can happen with conditions that affect the basal ganglia depend strongly on the type of condition:- Balance and coordination problems
- Muscle weakness and spasms
- Shakiness and tremors
- Vision problems
- Slurred speech
Movement disorders like Parkinson’s disease or Huntington’s disease will have different effects from carbon monoxide poisoning or heavy metal poisoning.
If your basal ganglia become dysfunctional — be it from stress, psychological issues, brain damage, or more subtle triggers — many problems can arise. The symptoms and health conditions you may experience as a result depend on several complex factors such as:
- Which part of the basal ganglia is affected
- Whether other parts of the brain are damaged
- If the whole structure or part of it is over- or under-active
- Your age, sex, and genetic predispositions
- Your overall health status
Reference:
Disorders of the Motor System (Section 3, Chapter 6) Neuroscience Online: An Electronic Textbook for the Neurosciences | Department of Neurobiology and Anatomy - The University of Texas Medical School at Houston. (2020). Tmc.edu. https://nba.uth.tmc.edu/neuroscience/m/s3/chapter06.html
Foster, J. (2020, January 17). Disorders & Diseases of the Basal Ganglia (incl. Stroke) - SelfDecode Health. SelfDecode Health. https://health.selfdecode.com/blog/basal-ganglia-disorders-stroke/
Clinic, C. (2022). Basal Ganglia: What It Is, Function & Anatomy - Cleveland Clinic. Cleveland Clinic. https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/body/23962-basal-ganglia




Comments
Post a Comment