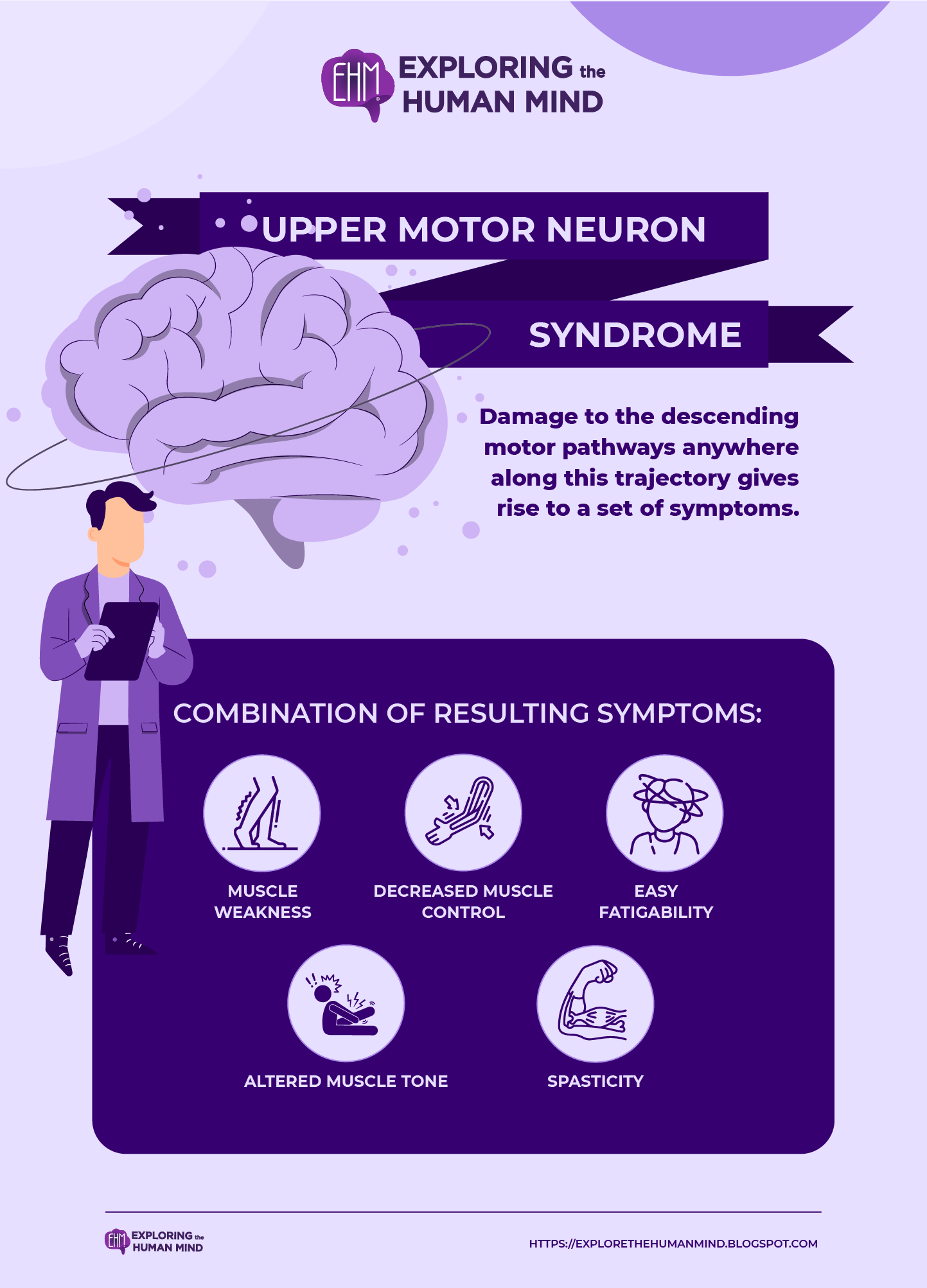
Upper Motor Neuron Syndrome
Upper motor neuron syndrome (UMNS) refers to changes in motor control that can occur in skeletal muscle following an upper motor neuron lesion.
vectors by Freepick; graphic design by Vadot
Performance Characteristics
Following upper motor neuron lesions, affected muscles may exhibit a variety of altered performance characteristics, including:- weakness (reduced muscle force generation ability)
- reduced motor control, including slower speed, accuracy, and dexterity
- Muscle tone changes (hypotonia or hypertonia): a decrease or increase in the level of muscle activity at rest
- reduced endurance
- Spasticity and clonus (a series of involuntary rapid muscle contractions) are examples of exaggerated deep tendon reflexes.
The term "upper motor neuron syndrome" refers to a collection of these symptoms. Affected muscles usually display a variety of symptoms, the severity of which is determined by the extent of damage and other factors influencing motor control. In neuroanatomical circles, for example, hemisection of the cervical spinal cord is frequently referred to as "upper lower motor neuron syndrome and lower upper motor neuron syndrome." The saying refers to lower motor neuron symptoms in the upper extremity (arm) and upper motor neuron symptoms in the lower extremity (leg).
Upper motor neuron injury is common because motor areas occupy a large portion of the cortex and motor pathways extend all the way from the cerebral cortex to the lower end of the spinal cord. Damage to the descending motor pathways at any point along this trajectory causes upper motor neuron syndrome.
Our movements are controlled by electrical and chemical signals that travel through the body's upper and lower motor neurons. Physical trauma, disease, or a lack of vitamins can all result in upper motor neuron lesions.
Early detection and treatment of the underlying cause or causes of upper motor neuron lesions can improve outcomes by reducing symptoms and slowing symptom progression.
Reference:
Upper Limb Reconstruction in the Upper Motor Neuron Syndrome Clinic: Overview (2022) Mayo Clinic; https://www.mayoclinic.org/departments-centers/upper-limb-reconstruction-umn-syndrome-clinic/overview/ovc-20466590
Wikipedia Contributors. (2023, June 6). Upper motor neuron syndrome. Wikipedia; Wikimedia Foundation. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Upper_motor_neuron_syndrome
Purves, D., Augustine, G. J., Fitzpatrick, D., Katz, L. C., LaMantia, A.-S., McNamara, J. O., & S Mark Williams. (2023). Damage to Descending Motor Pathways: The Upper Motor Neuron Syndrome. Nih.gov; Sinauer Associates. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK10898/
Dr David Bargiela. (2023, April 12). Upper vs Lower Motor Neurone Lesions | Signs | Geeky Medics. Geeky Medics. https://geekymedics.com/upper-vs-lower-motor-neurone-lesions/
Muscle disease - Types, Causes, Symptoms | Britannica. (2023). In Encyclopædia Britannica. https://www.britannica.com/science/muscle-disease/Classification-of-muscle-weakness#ref524135





Comments
Post a Comment