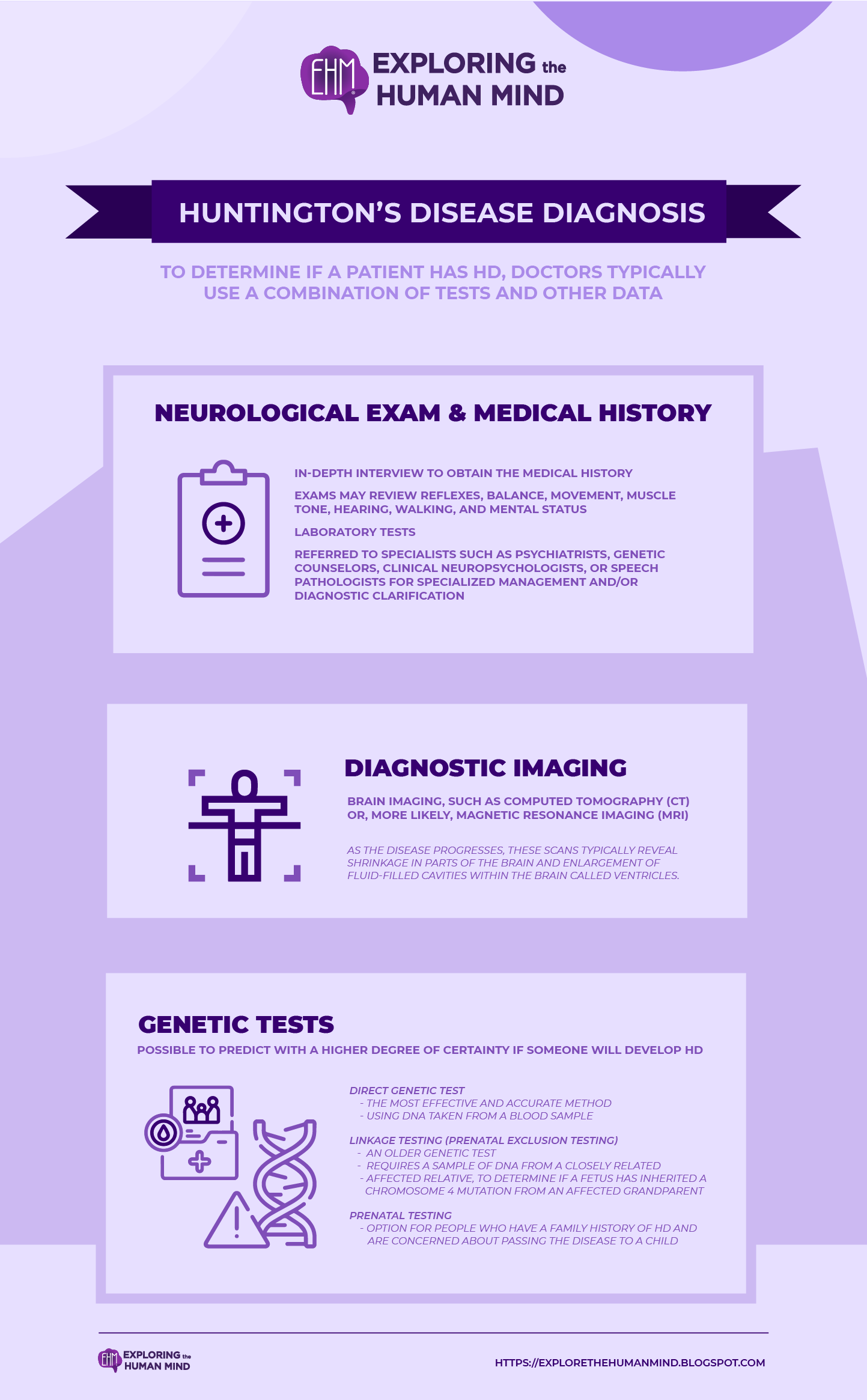
Huntington’s disease Diagnosis
Neurological exam and medical history—A neurologist will conduct an in-depth interview to obtain the medical history (including any family history, called a pedigree or genealogy) to rule out other conditions. Neurological and physical exams may review reflexes, balance, movement, muscle tone, hearing, walking, and mental status. Laboratory tests may also be ordered, and individuals with HD may be referred to specialists such as psychiatrists, genetic counselors, clinical neuropsychologists, or speech pathologists for specialized management and/or diagnostic clarification.
Diagnostic imaging—In some cases, especially if a person's family history and genetic testing are inconclusive, the physician may recommend brain imaging, such as computed tomography (CT) or, more likely, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). As the disease progresses, these scans typically reveal shrinkage in parts of the brain and enlargement of fluid-filled cavities within the brain called ventricles. These changes do not necessarily indicate HD, because they can occur in other disorders. A person can have early symptoms of HD and still have normal findings on a structural CT or MRI scan.
Genetic tests—Genetic testing can confirm or rule out a suspected genetic condition or help determine a person's chance of developing or passing on a genetic disorder. Genetic testing makes it possible to predict with a higher degree of certainty if someone will develop HD.
- The most effective and accurate method of testing for HD—called the direct genetic test—counts the number of CAG repeats in the HD gene, using DNA taken from a blood sample. The presence of 36 or more repeats supports a diagnosis of HD. A test result of 26 or fewer repeats rules out HD.
- An older genetic test, called linkage testing (also called prenatal exclusion testing) requires a sample of DNA from a closely related affected relative, preferably a parent, to identify markers close to the HD gene and to determine if a fetus has inherited a chromosome 4 mutation from an affected grandparent. A version of the linkage method is sometimes used for prenatal testing.
- Prenatal testing is an option for people who have a family history of HD and are concerned about passing the disease to a child. Prenatal testing can be done using either the direct method or the linkage method. As with adult testing, the direct method provides higher certainty.
vectors by Freepick; graphic design by Vadot
Reference:
Disorders of the Motor System (Section 3, Chapter 6) Neuroscience Online: An Electronic Textbook for the Neurosciences | Department of Neurobiology and Anatomy - The University of Texas Medical School at Houston. (2020). Tmc.edu. https://nba.uth.tmc.edu/neuroscience/m/s3/chapter06.html
Huntington’s Disease. (2023). National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke. https://www.ninds.nih.gov/health-information/disorders/huntingtons-disease#:~:text=Huntington%27s%20disease%20(HD)%20is%20an,as%20well%20as%20other%20areas.
Huntington disease: MedlinePlus Genetics. (2020). Medlineplus.gov. https://medlineplus.gov/genetics/condition/huntington-disease/#synonyms Huntington’s disease - Symptoms and causes. (2022). Mayo Clinic; https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/huntingtons-disease/symptoms-causes/syc-20356117





Comments
Post a Comment