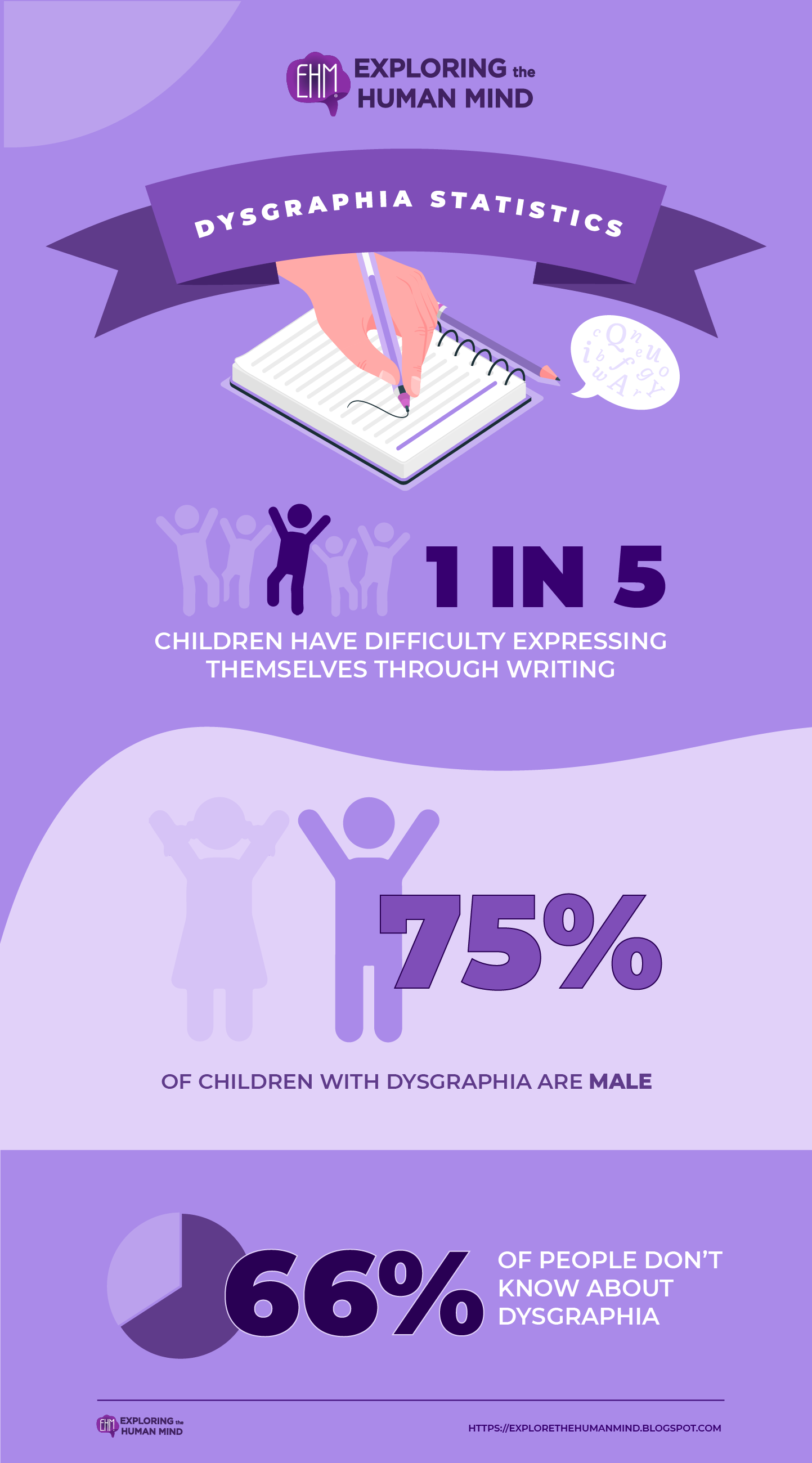
Dysgraphia Introduction
Dysgraphia is a neurological condition in which a person has difficulty translating their thoughts into written language for their age and cognitive ability, despite proper instruction and education.
Dysgraphia, also known as "written expression learning disorder," is a learning disability characterized by difficulty with written expression. Spelling, handwriting, and translating thoughts to paper can all be affected by dysgraphia.
Individuals with dysgraphia may find it difficult to form letters, numbers, and words by hand, as well as to think and write at the same time. In more severe cases, the student may be unable to draw a straight line or hold a pencil correctly.
vectors by Freepick; graphic design by Vadot
Writing requires complex skills that involve vision, movement, and the ability to process information. A learning disorder in writing, also called dysgraphia, may cause the following:
- Slow handwriting that takes a lot of work
- Trouble recalling how to form letters, copy shapes and draw lines
- Handwriting that's hard to read
- Trouble putting thoughts into writing
- Written text that's poorly organized or hard to understand
- Trouble with spelling, grammar and punctuation
Dysgraphia typically manifests itself when children are first learning to write. This is referred to as developmental dysgraphia. Dygraphia can also occur unexpectedly following a head or brain trauma. This is known as acquired dysgraphia.
Reference:
Churchillstl Design. (2017, February 17). Churchillstl Design. https://www.churchillstl.org/learning-disability-resources/dysgraphia/
Know the signs of learning disorders in kids. (2023). Mayo Clinic. https://www.mayoclinic.org/healthy-lifestyle/childrens-health/in-depth/learning-disorders/art-20046105
Clinic, C. (2022). Dysgraphia: What It Is, Symptoms, Diagnosis & Treatment - Cleveland Clinic. Cleveland Clinic. https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/23294-dysgraphia






Comments
Post a Comment