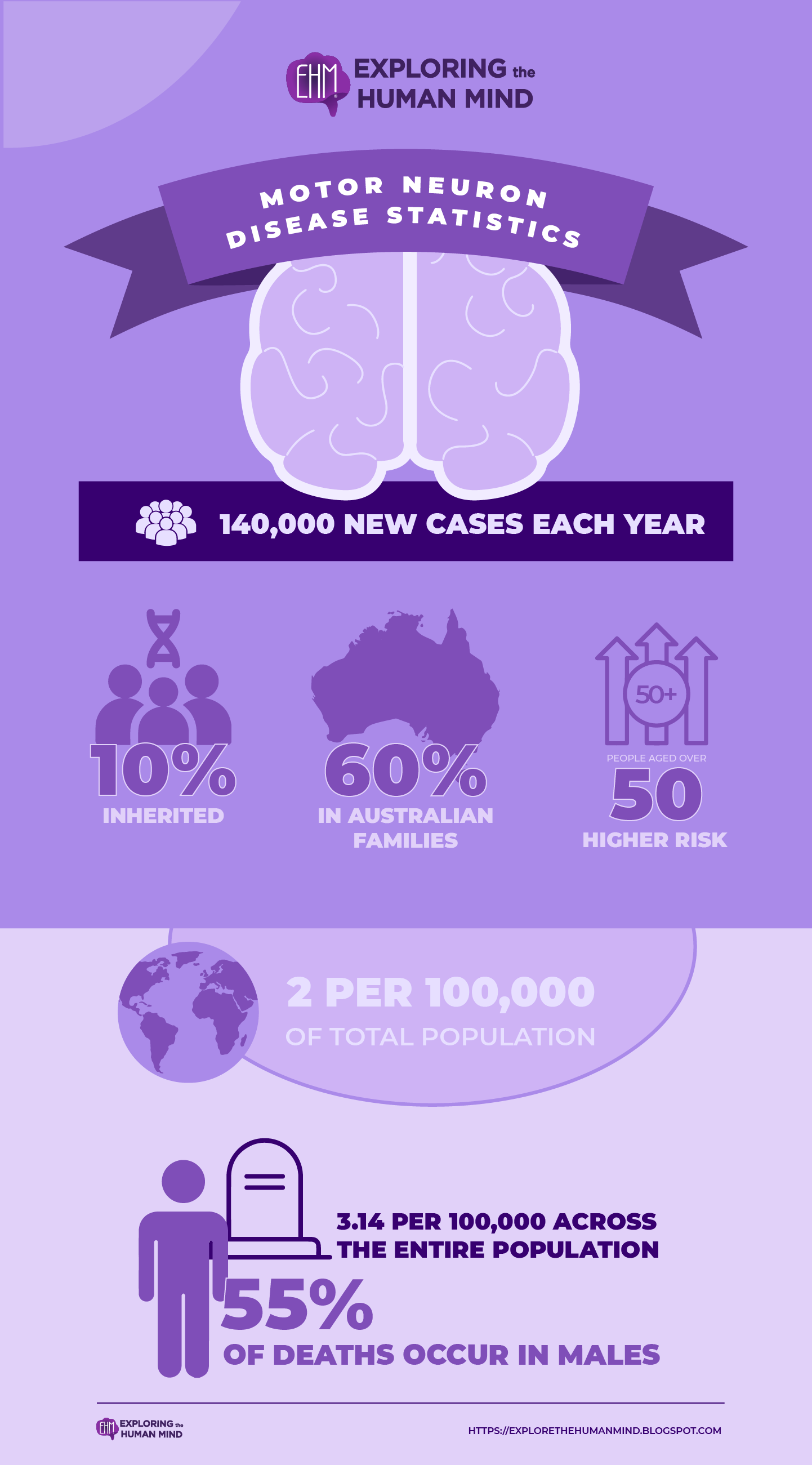
Motor Neuron Syndrome Statistics
MND occurs in every country on the planet. The incidence and prevalence of MND are commonly used to assess the disease's impact on the community. The number of new cases added in a given time period, usually a year, is referred to as the incidence. Prevalence is the number of cases that exist at any given time.
vectors by Freepick; graphic design by Vadot
Statistics
Most of these cases is now known in Australian families. However, new research indicates that many sporadic cases have a genetic component.The incidence is 2 per 100,000 of the total population worldwide, while the prevalence is around 6 per 100,000 of the total population. According to research, the incidence is higher in people over the age of 50. Despite being classified as a rare disease in terms of prevalence, it is estimated that approximately 140,000 new cases are diagnosed globally each year. The lifetime risk of developing ALS/MND has been calculated to be one in three hundred.
MND mortality rates are relatively high in all age groups. The overall mortality rate is estimated to be 3.14 per 100,000 people. Males account for approximately 55% of all fatalities. MND-related deaths are typically caused by respiratory failure caused by weakened respiratory muscles.
Reference:
Motor Neurone Disease Information & Support | MND Australia | MND Australia. (2015). Mndaustralia.org.au. https://www.mndaustralia.org.au/mnd-connect/for-health-professionals-service-providers/overview-of-mnd-for-health-professionals





Comments
Post a Comment