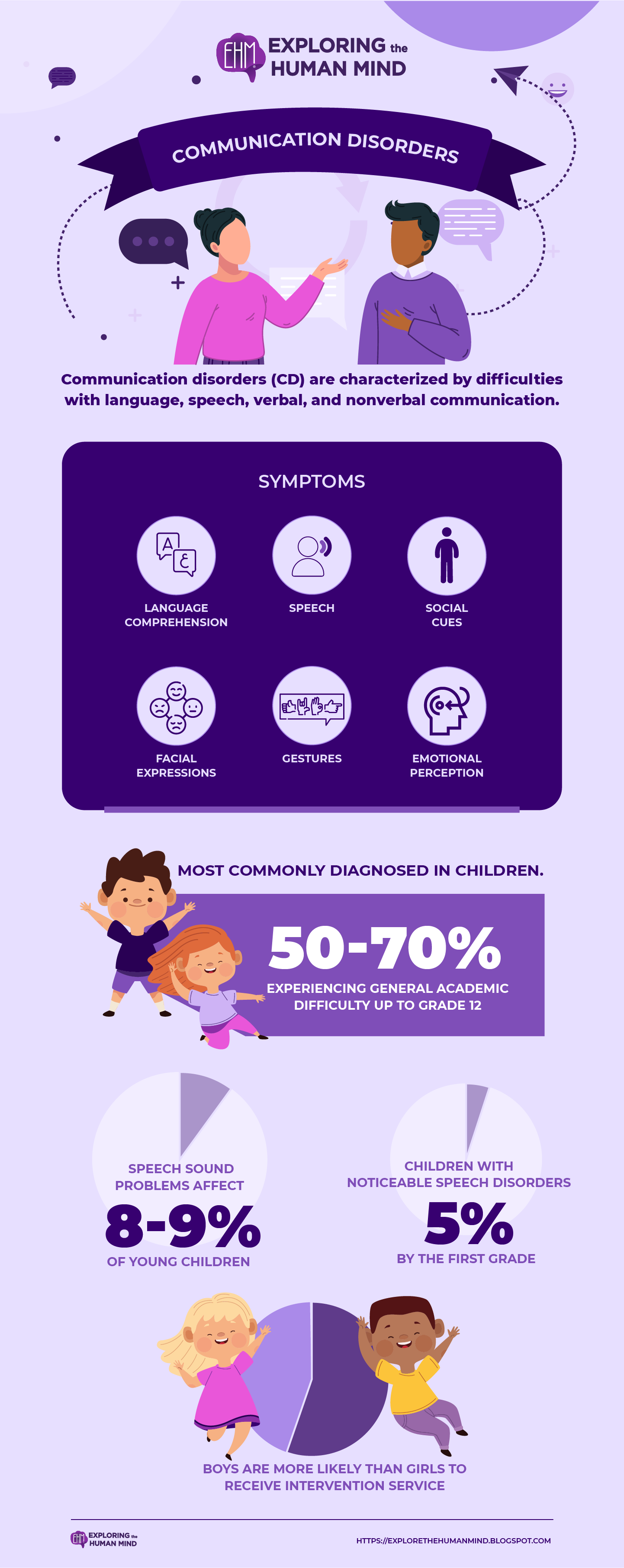
Communication Disorders Intro
Symptoms
CDs symptoms are usually graded on a scale, with mild to severe impairments. They also tend to coexist when a person has been diagnosed with multiple types of CDs. Most suffer from common communication impairments in both verbal and nonverbal communication, with difficulties in the following areas:
- Language comprehension
- Speech
- Social cues
- Facial expressions
- Gestures
- Emotional perception
Causes
Although there is no single cause of CDs, genetic factors and factors influencing brain development during the early developmental period may play a role.
Diagnosis
A person must meet the diagnostic criteria outlined in the fifth edition of the The Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM-5) and other mental health classification books to be diagnosed with a CD.
The most recent CD included in this diagnostic manual was social (pragmatic) communication disorder (SCD), in an attempt to distinguish this isolated communication disorder from the current autism spectrum disorder (ASD) diagnosis, which includes social communication difficulties and restrictive/repetitive behaviors.
vectors by Freepick; graphic design by Vadot
Statistics
- In 28-60% of children with a speech and language deficiency, a sibling or parent is affected.. Speech sound problems affect 8-9% of young children.
- By the first grade, about 5% of children have noticeable speech disorders, with the vast majority going undiagnosed.
- Additional services are frequently required for children with phonological disorders, with 50-70% experiencing general academic difficulty up to grade 12.
- Boys (ages 3-17) with a voice, speech, language, or swallowing disorder are more likely than girls to receive intervention services (59.4 percent vs. 47.8 percent).
- Among children aged 3 to 17 who have a voice, speech, language, or swallowing disorder, those with speech or language problems are more likely to receive intervention services than those with a voice disorder (22.8 percent) or swallowing problems (12.7 percent).
Communication disorders are most commonly diagnosed in children. CDs can have an impact on both adults and children. However, the vast majority of social impairment research has been conducted on toddlers, children, and adolescents.
CDs are most easily identified in childhood, when the child can benefit from therapy to help develop communication and social skills.
Adults may have a more difficult time detecting and treating these impairments because they are no longer developmental concerns, but rather social habits that disrupt communication and societal norms.
Reference:
https://www.facebook.com/verywell. (2022). What to Know About Different Types Communication Disorders. Verywell Mind. https://www.verywellmind.com/communication-disorder-types-5220602#toc-types-of-communication-disorders
Speech, C. (2021, August 3). Facts About Communication Disorders. Columbus Speech and Hearing. https://columbusspeech.org/facts-about-communication-disorders/
Quick Statistics About Voice, Speech, Language. (2016, May 19). NIDCD. https://www.nidcd.nih.gov/health/statistics/quick-statistics-voice-speech-language






Comments
Post a Comment